Lumbar Facet Syndrome (FAQs)
- thepainreliefmd
- Mar 2, 2024
- 2 min read
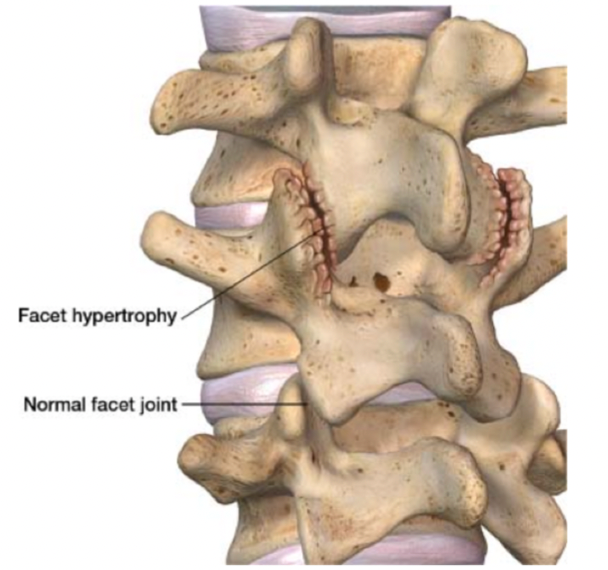
What are lumbar facet joints?
The lumbar facet joints are small joints that act as hinges in our back, connecting all the vertebral bones yet still allowing us to bend and twist with ease. These joints are a common cause of low back pain.
What is lumbar facet syndrome and its symptoms?
Lumbar facet syndrome refers to a clinical condition consisting of various symptoms, including low back pain radiating to either one or both buttocks, sides of the groin,
and thighs, stopping above the knee. It should, however, be
noted that in some cases, the symptoms of facet-mediated
pain may mimic symptoms of “sciatica” occurring from herniated
discs or compressed nerve roots.
What causes lumbar facet syndrome?
The facet joint degenerates with repetitive overuse and everyday activities, eventually degenerative osteoarthritis of the facet joint. This notion is supported by the strong association between the incidence of facet joint arthritis and increasing age. There are also strong associations between intervertebral disc degeneration, spondylolisthesis (when the vertebra slips out of place), and facet joint arthritis.
How is lumbar facet syndrome treated?
Treatment for lumbar facet syndrome usually start with a conservative approach. If conservative options fail, then injections are often necessary. Conservative treatments op6ons include medication such as NSAIDs (i.e., Ibuprofen, naproxen), acetaminophen, and oral steroids during acute flares. Additionally, weight loss and physical therapy have demonstrated successful outcomes. Physical therapy includes lumbosacral stretching and strengthening, as well as core strengthening. Application of heat, ice, deep tissue massage, myofascial release can also be helpful. Patients who fail conservative treatment may undergo a diagnostic medial branch nerve block. In patients with successful diagnostic blocks, radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or peripheral nerve stimulation can be performed.
What is a diagnostic medial branch nerve block?
A diagnostic medial branch block is a test to determine the cause of your low back pain. It is important to note that diagnostic blocks are not intended to treat the painful condition - its purpose is to determine the source of your low back pain. The block involves injecting local anesthetic (i.e., Lidocaine) near the medial branch nerves. Because the medial branch nerves supply the facet joints, blocking the medial branch nerve with a local anesthetic would inhibit the transmission of painful signal from reaching the brain where pain is perceived. Diagnostic blocks are not intended to last long as it typically only last about 6-8 hours. If you experience significant reduction of your typical low back pain for approximately 6-8 hours after your diagnostic medial branch block, then the cause of your low back pain is most likely due to facet joint disease. After two positive diagnostic blocks, a definitive treatment option is utilized to provide long-lasting pain relief of facet-mediated low back pain. .

Comments